History of Tea Cultivation
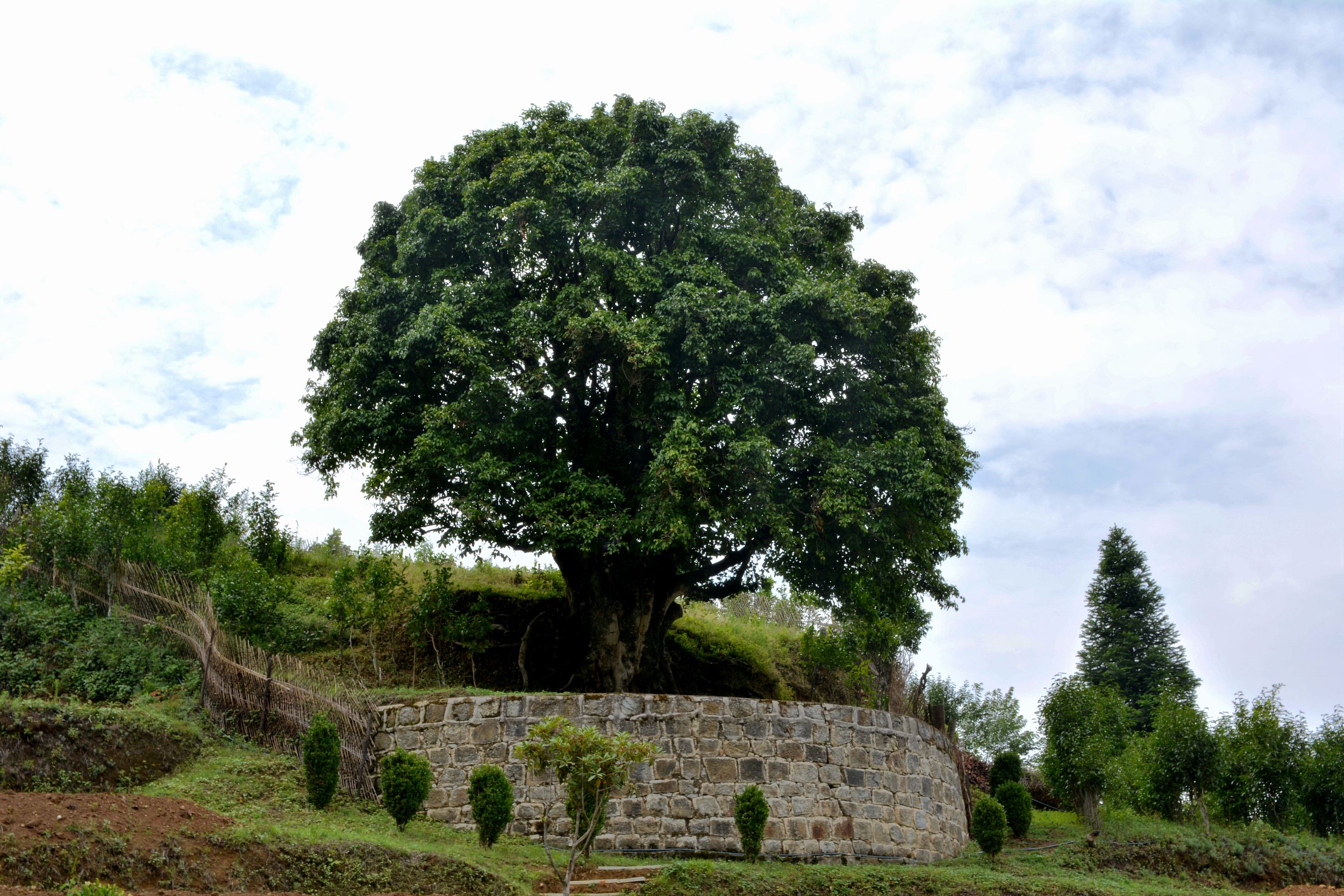

The picture taken on July 11, 2015 shows a 3,200-years-old tea tree at Jinxiu Village, Lincang City, Yunnan Province. (PHOTO:VCG)
By BI Weizi
Tea is one of the most popular non-alcoholic beverages in the world. China is where tea originated, and the Chinese were the first people in the world to develop the habit of drinking tea.
Tea was domesticated over 3,000 years ago and was one of the earliest varieties of trees in China. Recent excavations of the "Han Yang Tomb" in Xi'an, Shaanxi province, have revealed that the emperors of the Han Dynasty were fond of tea, providing strong evidence that China has a long history of tea cultivation.
Since then, tea has not only become a tribute to the imperial court, but also an important commodity for the exchange of horses from Western Asia. In the late Ming and early Qing dynasties, an official road from Pu'er to Kunming was built to facilitate trade. This caravan road was known as the ancient Tea Horse Road, and later in the West as the Southern Silk Road.
Although tea production, processing techniques and tea drinking practices were already quite common, the specific methods of tea cultivation were not well documented until the Tang Dynasty, with Lu Yu's The Classic of Tea, the first known monograph on tea, honoring the beverage as the harmony and mysterious unity of the universe.
During the Ming and Qing dynasties, the transplanting method of weed control for wet or muddy fields, and the asexual propagation method, including cuttings, layering, division, budding and grafting, was adopted in the cultivation of tea trees, which made a significant contribution to the popularity of tea throughout the world.